Infrastructure as code with Terraform
Created by Stéphane Cusin
My first VPS Server

What append when I should change infrastructure ?
Move to another provider
Ok, I don't will do it again
Provisioning servers with ansible, but all infrastructure was made by hand.
Provisioning with ansible
Today, how to deploy a new project.

We can use AWS
Or Google Cloud Platform
You probably want more than one server
ok but infrastructure is not only server
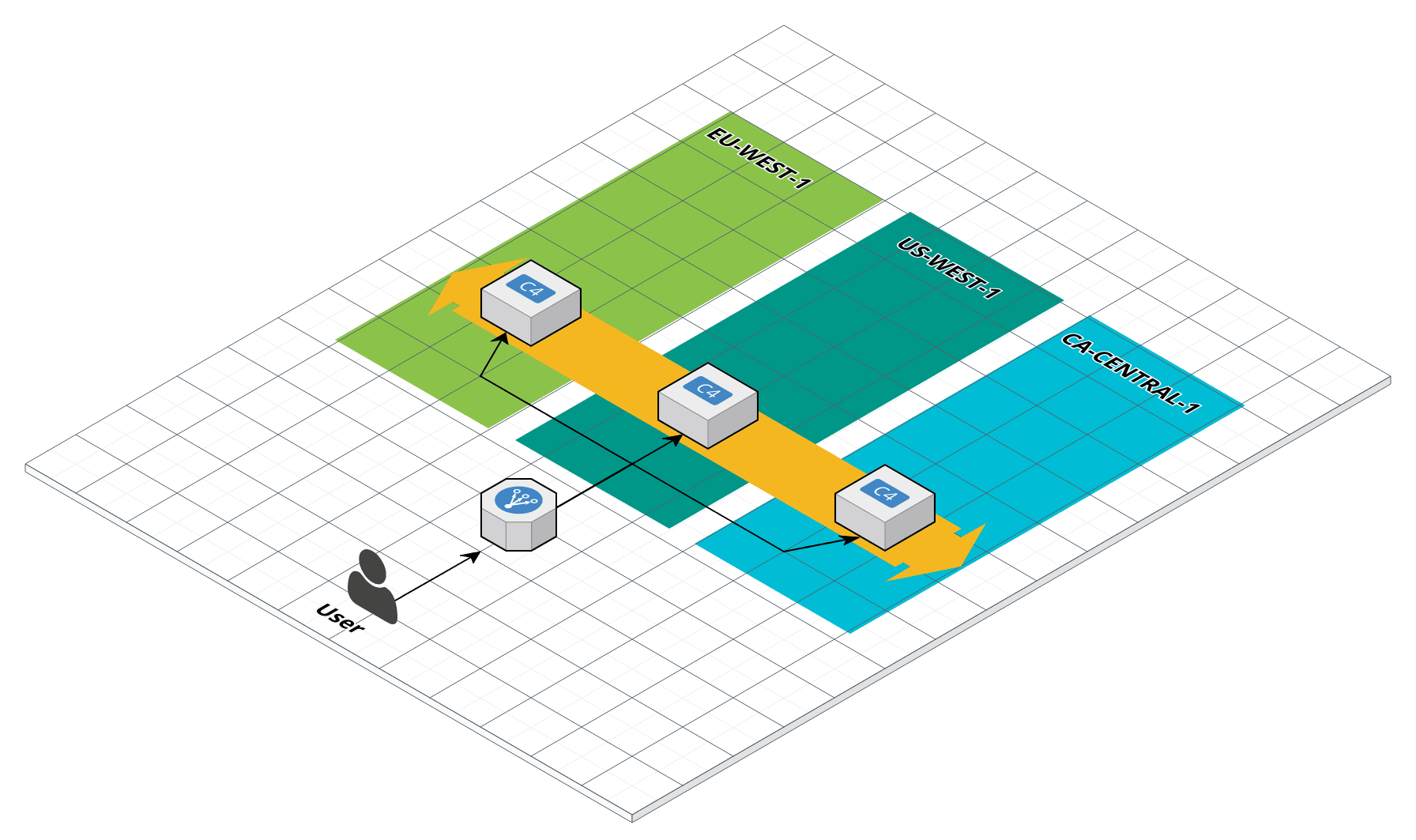
Add a load balancer
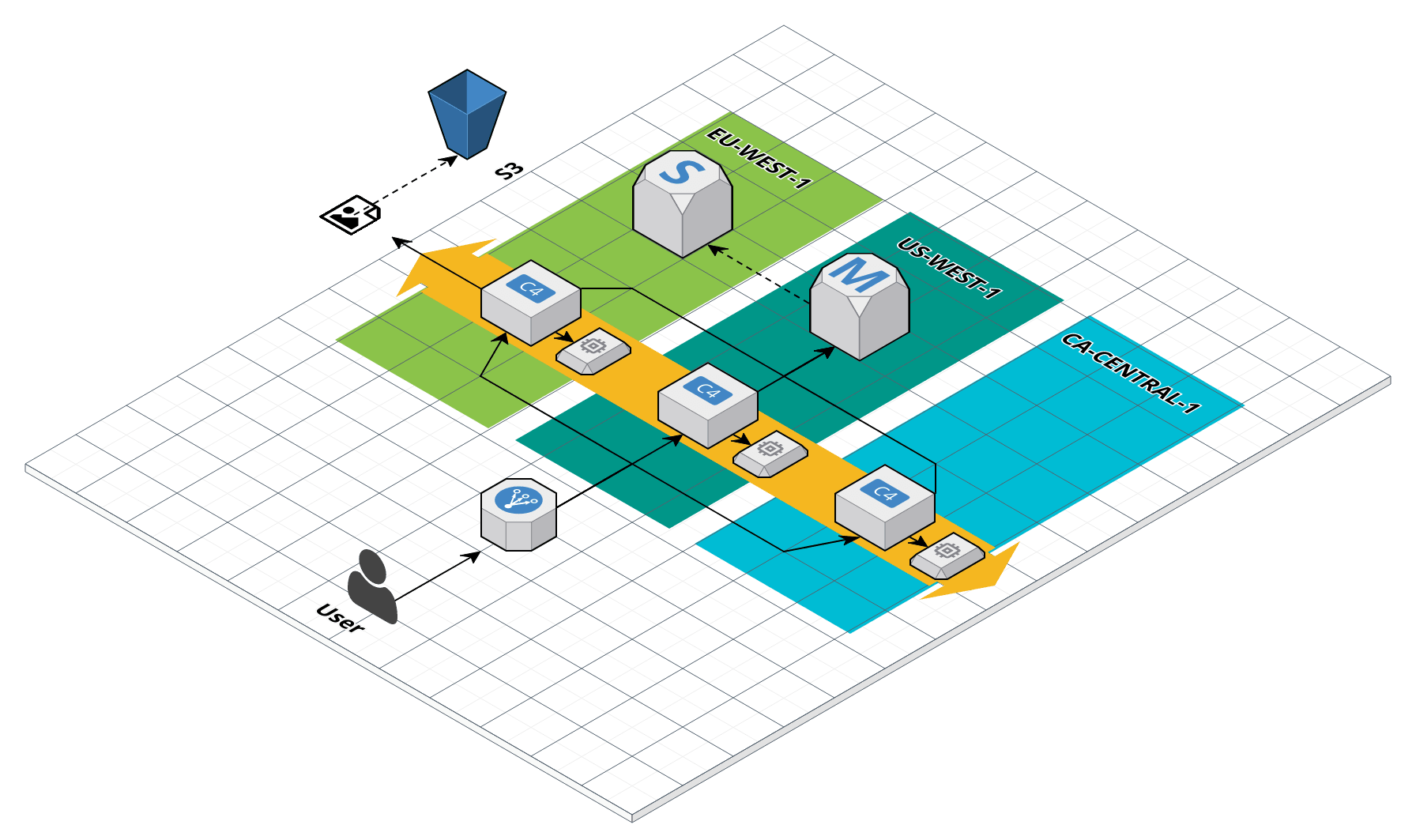
And Volumes, databases and S3 to store all data

Don't forget the VPC, subnets, route tables, Nat gateways
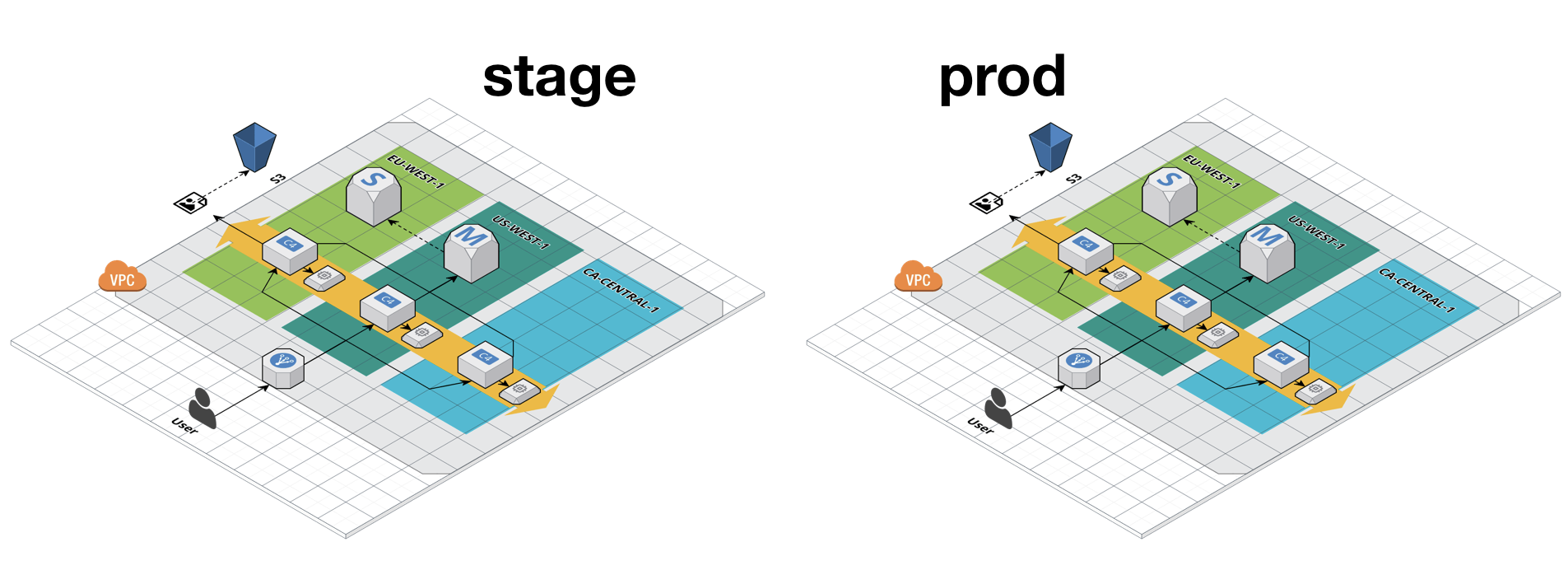
And you should have that in separate environments for stage and prod
What append if all was setup with web UI and
you have to maintain it all. Forever
In this talk, I will show you how to use infrastructure as code to deploy Kubernetes over Openstack.
In just a few simple commands
$ wayoos-source-prod
$ infra-compose exec up
I'm
Stéphane
Cusin
wayoos.io
github.com/wayoos
Outline
1. infrastructure as code
2. terraform
3. demo
4. infra-compose
Outline
1. infrastructure as code
2. terraform
3. demo
4. infra-compose
Instead of clicking around a web UI or SSHing to a server and manually executing commands, the idea behind IAC is to write code to define, provision, and manage your infrastructure.
The benefits of infrastructure as code
- Treat Infrastructure Like Application Code
- Same Code for All Environments
- Anyone Can Build an Environment Anytime
- Validate Infrastructure Before Deployment
- Always Know What Changed
- Iac Will Put a Smile on Your Face
Ok for IAC but which tool ?
- Puppet (2005)
- Chef (2009)
- SaltStack (2011)
- CloudFormation (2011)
- Ansible (2012)
- Terraform (2014)
Why I use Terraform
- Configuration Management vs Orchestration
- Procedural vs Declarative
- Mutable Infrastructure vs Immutable Infrastructure
- Client/Server Architecture vs Client-Only Architecture
Configuration Management vs Orchestration
Chef, Puppet, Ansible, and SaltStack are all “configuration management” tools, which means they are designed to install and manage software on existing servers.
Configuration Management vs Orchestration
CloudFormation and Terraform are “orchestration tools”, which means they are designed to provision the servers themselves, leaving the job of configuring those servers to other tools.
Procedural vs Declarative
Chef and Ansible encourage a procedural style where you write code that specifies, step-by-step, how to achieve some desired end state.
Java analogy: ant
Procedural vs Declarative
Terraform, CloudFormation, SaltStack, and Puppet all encourage a more declarative style where you write code that specifies your desired end state, and the IAC tool itself is responsible for figuring out how to achieve that state.
Java analogy: maven
Mutable Infrastructure vs Immutable Infrastructure
Configuration management tools such as Chef, Puppet, Ansible, and SaltStack typically default to a mutable infrastructure paradigm.
Mutable Infrastructure vs Immutable Infrastructure
If you’re using an orchestration tool such as Terraform to deploy machine images created by Docker or Packer, then every “change” is actually a deployment of a new server.
Client/Server Architecture vs Client-Only Architecture
Chef, Puppet, and SaltStack all use a client/server architecture by default. The client, which could be a web UI or a CLI tool, is what you use to issue commands.
Client/Server Architecture vs Client-Only Architecture
CloudFormation, Ansible, and Terraform, use a client-only architecture.
A comparison of popular infrastructure as code tools
| Puppet | Chef | SaltStack | CloudFormation | Ansible | Terraform | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Code | Open source | Open source | Open source | Closed source | Open source | Open source |
| Cloud | All | All | All | AWS only | All | All |
| Type | Config Mgmt | Config Mgmt | Config Mgmt | Orchestration | Config Mgmt | Orchestration |
| Language | Declarative | Procedural | Declarative | Declarative | Procedural | Declarative |
| Infrastructure | Mutable | Mutable | Mutable | Immutable | Mutable | Immutable |
| Architecture | Client/Server | Client/Server | Client/Server | Client-Only | Client-Only | Client-Only |
Outline
1. infrastructure as code
2. terraform
3. demo
4. infra-compose
Terraform enables you to safely and predictably create, change, and improve infrastructure. It is an open source tool that codifies APIs into declarative configuration files that can be shared amongst team members, treated as code, edited, reviewed, and versioned.
terraform.io (HashiCorp)
How's that work?
- .tf config file allows teams to describe their infrastructure in simple DSL
- terraform CLI creates, changes, and destroys these resources accordingly
Declare .tf file resources via HCL (HashiCorp Configuration Language)
resource "openstack_compute_instance_v2" "bastion" {
name = "bastion"
image_id = "${data.openstack_images_image_v2.bastion.id}"
flavor_id = "${var.flavor_id_s1_2}"
key_pair = "bastion-key"
security_groups = ["bastion"]
network {
name = "Ext-Net"
access_network = "true"
}
}
Basic CLI usage
- terraform plan to view the execution plan
- terraform apply to execute the plan
- terraform destroy to destroy infrastructure
Outline
1. infrastructure as code
2. terraform
3. demo
4. infra-compose
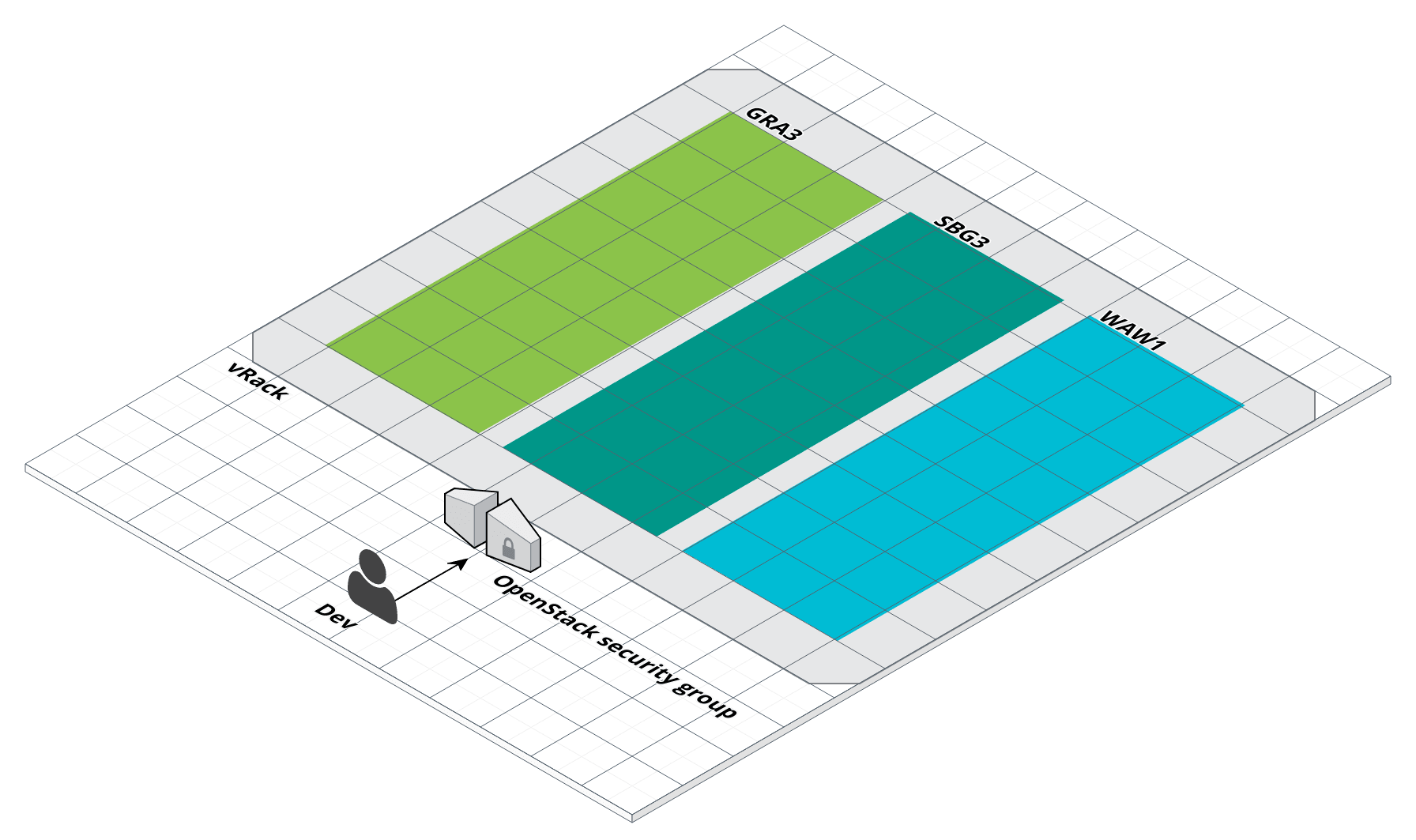
First things define network setup
Network setup, vrack and security group
$ infra-compose exec ovh-vrack up
$ infra-compose exec network-up
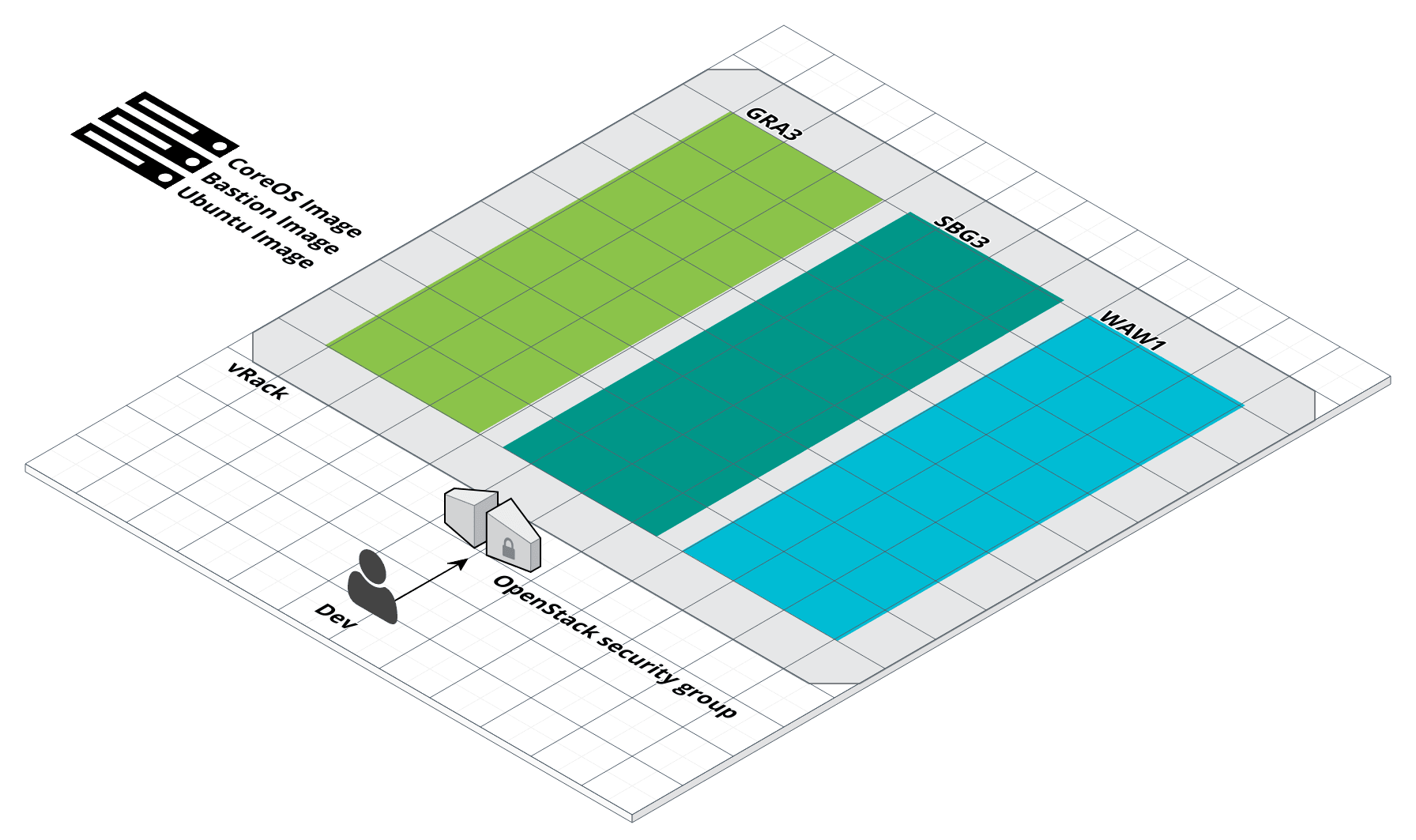
Control base server image
Install server images
$ infra-compose exec image-up
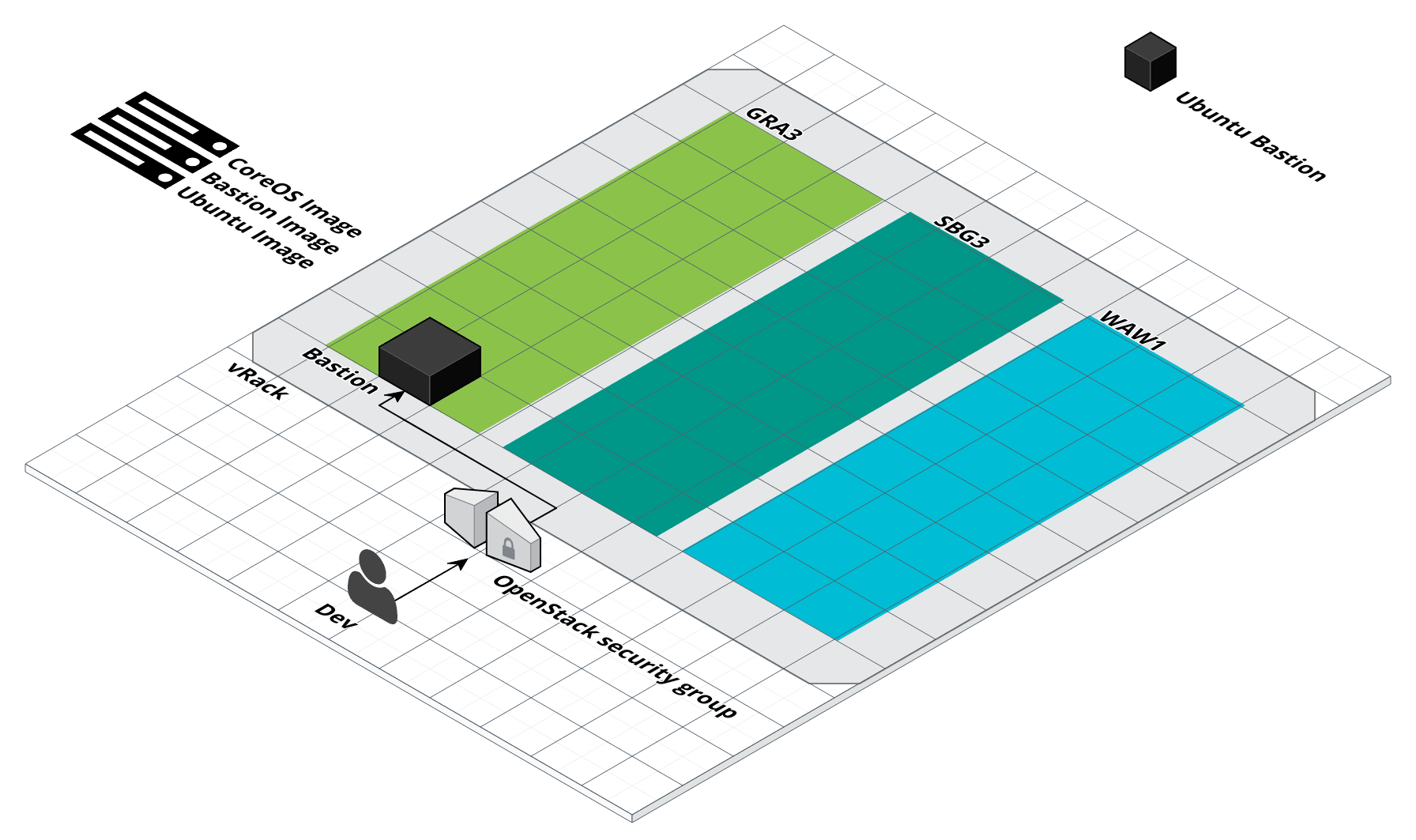
Bastion
Start bastion
$ infra-compose exec bastion up
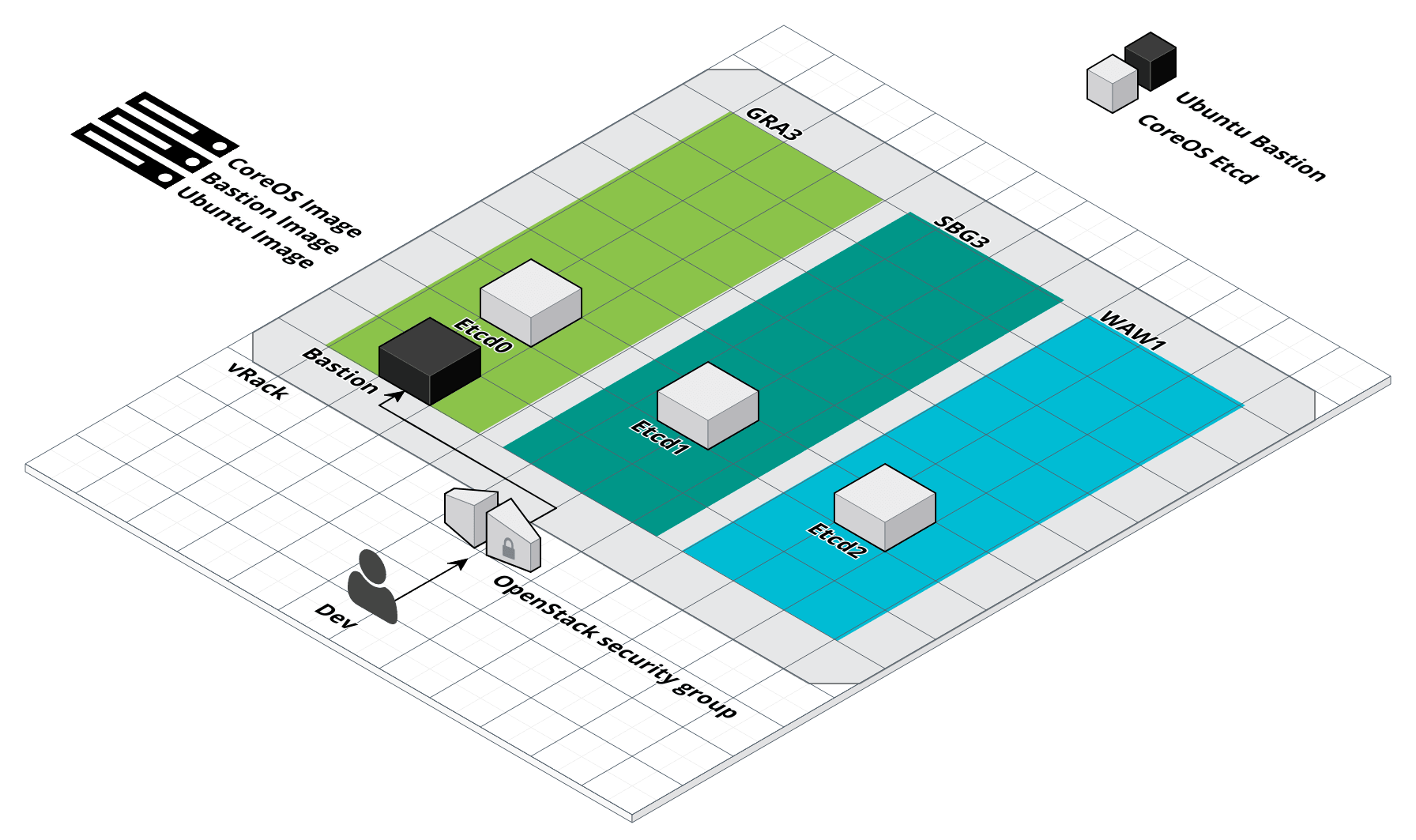
Etcd cluster
Start Etcd cluster
$ infra-compose exec etcd-new
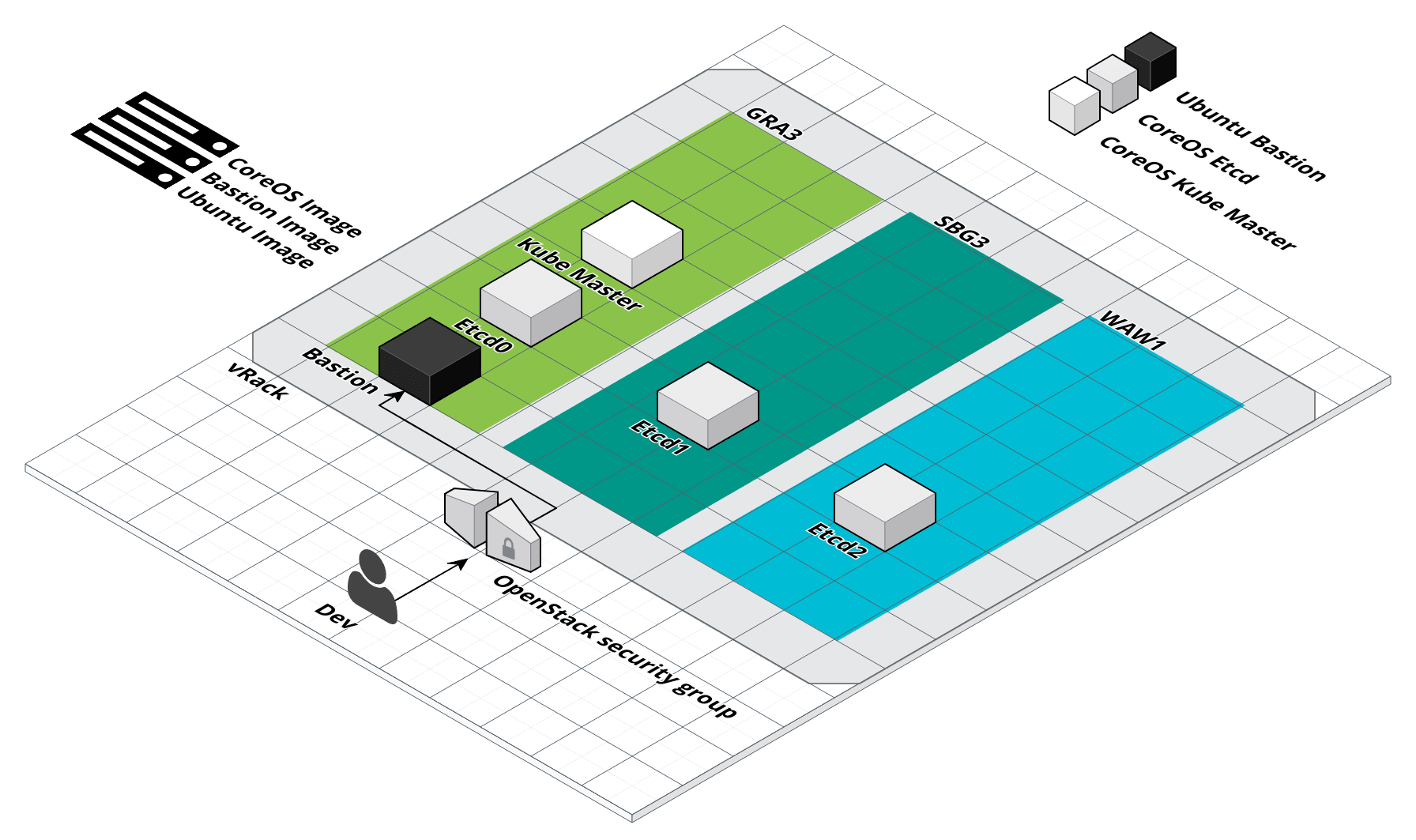
Kubernetes master
Start Kubernetes master
$ infra-compose exec kube-master up
Start Kubernetes workers
$ infra-compose exec kube-worker0 up
$ infra-compose exec kube-worker1 up
$ infra-compose exec kube-worker2 up
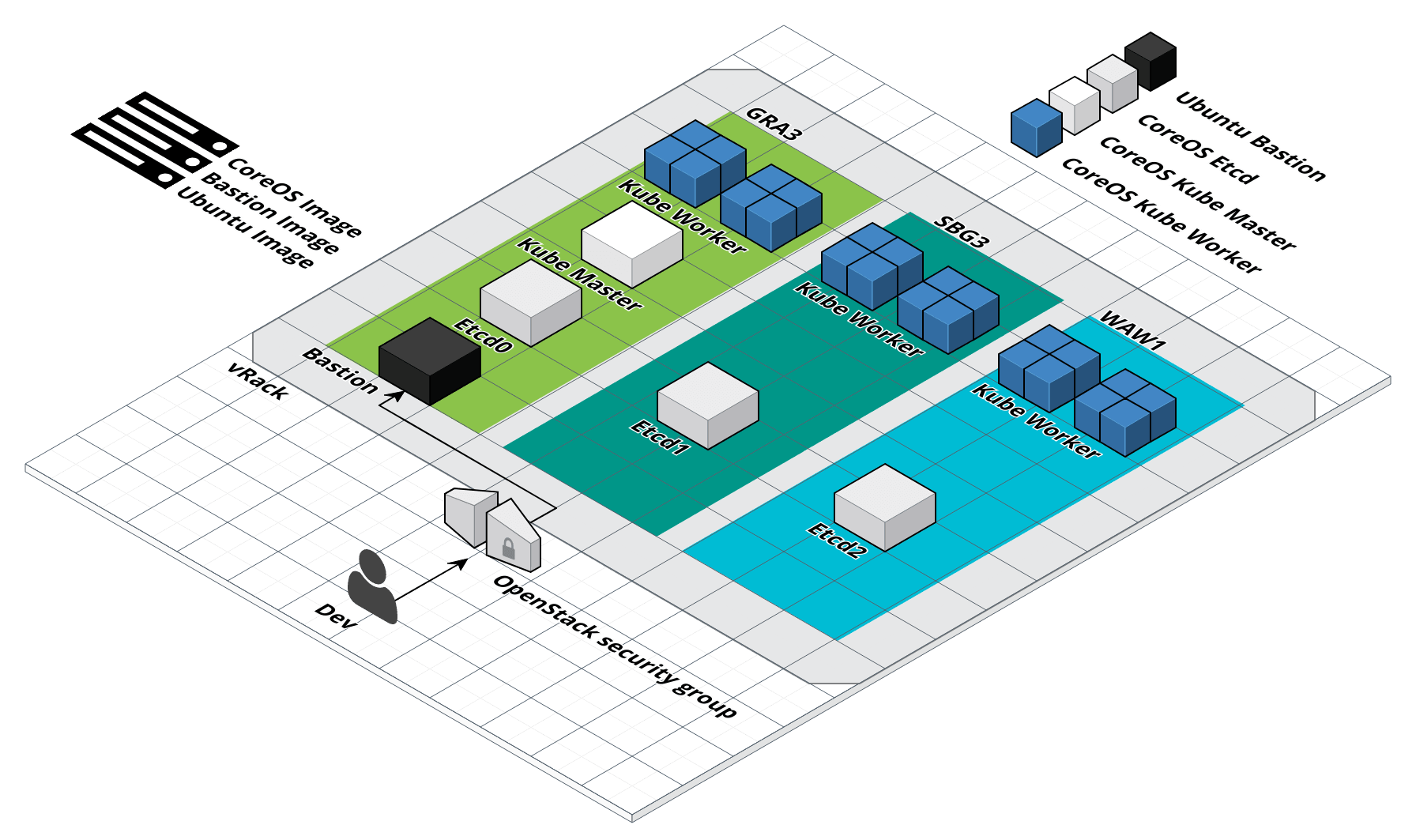
Final infrastructure, managed by code
The price of this setup
- Bastion 3€
- Etcd server 3x 6€
- Kube master 6€
- Kube worker 24x 20€
For 507€ you will have a kubernetes cluster of 2x24=48 Cores and 7Gbx24=168
Outline
1. infrastructure as code
2. terraform
3. demo
4. infra-compose
infra-compose is a tool for defining and running infrastructure commands. With infra-compose, you use a Compose file to configure your application's services. Then, using a single command, you create and start all the infrastructure for your applications.
infra-compose.yaml example
version: '1'
environments:
europe:
- OS_REGION_NAME=EUR
USEast:
- OS_REGION_NAME=US-EAST
services:
bastion:
path: mgmt/services/bastion
commands:
init: [terraform init]
up: [terraform apply]
down: [terraform destroy -force]
ssh: [./script-ssh-connect.sh]
commands:
init:
- global init
- bastion init
up:
- europe global up
- USEast global up
- bastion up
down: [bastion down]
infra-compose exec europe bastion up
infra-compose exec USEast bastion up
First release start 2018
Welcome all kinds of contributions